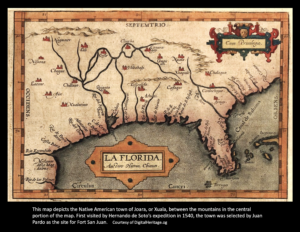
Fort San Juan, the earliest European settlement in the interior of what is now the U.S. was built in the town of Joara/Xuala (the Berry archeological site) near Morganton in western North Carolina. African-descended Iberians and Africans may have been part of the expedition (no archival records state this but can be inferred from the initial expedition and expeditions of their kind), suggesting early contact and an African Diasporic presence in the Carolinas prior to the seventeenth century.
Fort San Juan, the earliest European settlement in the interior of what is now the U.S. was built in the town of Joara/Xuala (the Berry archeological site) near Morganton in western North Carolina. African-descended Iberians and Africans may have been part of the expedition (no archival records state this but can be inferred from the initial expedition and expeditions of their kind), suggesting early contact and an African Diasporic presence in the Carolinas prior to the seventeenth century.
Joara Foundation
Between 1566 and 1567, Juan Pardo, a Spanish explorer and conquistador, following the earlier example of Hernando de Soto (who passed through the Berry site in 1540), led two expeditions into the Carolina and Tennessee mountains. His objective was to claim land for Spain, and especially to discover an overland route to Spain’s silver mines in Mexico. Pardo constructed Fort San Juan near present day Morganton, North Carolina, along with two other forts. But faced with the threat of an Indian attack on the Tennessee slopes of the Great Smoky Mountains, he decided to turn back. His retreat marked the end of Spain’s attempt to find a land route to Mexico through Appalachia, and his three forts were slowly abandoned. By the 18th century, Britain replaced Spain as the colonial power in southern Appalachia.
In December 1566, Juan Pardo left the Spanish town of Santa Elena on the South Carolina and traveled into North Carolina with 130 men in search of an overland route to Mexico. During his march, he built a string of small forts between modern day Beaufort, South Carolina, and what is now western Tennessee. Scholars have debated about the routes of Pardo and de Soto for years, but research at the Berry site provides evidence that both of these expeditions passed through the upper Catawba Valley of North Carolina.
Spanish soldiers lived at Fort San Juan for 18 months, from January 1567 until about June 1568. During the spring of 1568, relations between the Spaniards and the native peoples of Joara/Xuala ended with a Native American uprising and the fort was burned and destroyed.

[Images: Map with “Xuala” shown as part of the series of Spanish forts; photo of Native American dance at 450th anniversary of the building of Fort San Juan; piece of pottery with team from October 29, 2022, public dig; Omar Ali standing with New River Catawba Chief Lightwalker (Iggli Iggli Auoti Napaha)]
WORLD HISTORY TIMELINE
A work-play in progress (updated 1/26/2025) …
13.8 billion years ago
Universe appears. Sensitive radio telescope technology which shows faint cosmic microwave background radiation is detected in 1964. Radio telescopes are observing instruments used in radio astronomy, which studies the radio frequency portion of the electromagnetic spectrum emitted by astronomical objects, just as optical telescopes are used in traditional optical astronomy which studies the light wave portion of the spectrum coming from astronomical objects.
Protons and electrons form sometime within the first second but it takes 370,000 years for the first atoms to form as Hydrogen (needed to cool down sufficiently to form stable atoms from high energy plasma state). It then takes another 200,000,000 for the first stars and galaxies to form (where there’s more stuff, there’s more gravity … which is how stars are formed)
4.5 billion years ago
Our solar system comes into existence with earth. How do we know? We’ve used the debris from meteor impacts, such as the Meteor Crater in Arizona, assuming that the material from such meteors coming from the asteroid belt would have been made at the same time as the Earth.
3.5 billion years ago
Prokaryotes, single-cell organisms without a nucleus, appear in fossil record. They are the first living organisms. The name comes from the Greek ‘pro’ (before) ‘karyon’ (nut or kernel), since it lacks a membrane-bound nucleus.
1.5 billion years ago
Eukaryotes, multicellular organism with nucleus, appear in fossil record, among the first of these being algae.
530 million years ago
Cambrian Explosion would see super biodiversity on earth. Tardigrades, ‘slow walkers,’ appear around in the fossil record (discovered in 1773 by a German pastor named Johann Goeze).
500 million years ago
Plants move to land.
65 million years ago
Asteroid hitting the Yucatán peninsula wipes out dinosaurs, as part of one of five major extinction events. Mammals and birds, the latter descended from theropod (carnivorous, bipedal) dinosaurs, emerged as dominant large land animals. Georges Cuvier in early 19th century is first to establish notion of extinction and identify dinosaurs through fossil evidence. We may be currently living through one of the biggest extinction events as our human population displaced and destroys other species. We have succeeded to increase our carrying capacity through agricultural production, medical advancements, and public health measures—yet our population is now slowing down since there is less need for children as labor. We have moved from positive feedback loop to negative with 1.1% growth (slowing down since 1960s).
55 million years ago
Proto-primates become social
14 million years ago
Proconsuls
6 million years ago
Last common ancestor to what would become chimpanzees and hominin diverge genetically. Based on an estimation on fossil evidence and molecular clock techniques, which analyze differences in DNA sequences between species.
4.4 million years ago
Early hominin, “Ardi” (Ardipithecus ramidus) found in Afar region, Ethiopia.
3 million years ago
Lucy, Australopithecus afarensis, ‘Southern ape from Afar,’ is uncovered in Ethiopia.
2 million years ago
Homo Erectus, followed by Homo Habilis, and later Neanderthal, appear. Discoveries of the former made by Louis, Mary, and son, Richard Leakey in Olduvai Gorge, northern Tanzania.
1 million years ago
Homo Erectus gains control of fire, tool-making well underway among Neanderthals (either H. neanderthalensis or as H. s. neanderthalensis)
250,000 years ago
Modern humans (Homo sapiens sapiens) appear in Eastern Africa; we are foragers, nomadic hunters and gatherers.
Beginning of Paleolithic (‘Old Stone Age’), the great stretch of human history, till the Mesolithic about 20,000 years ago.
100,000 years ago
Out of Africa. Humans begin migration out of Africa to Eurasia, and will populate the world, albeit in very small numbers.
20,000 years ago
Humans reach the Americas, traveling down coast to South America drawing on kelp.
12,000 years ago
Neolithic Revolution (‘new stone age’), with tools that are more polished. Up to this point, since 200,000, most of human history, small communities, with global migration, little population growth. We cultivated grains in Mesopotamia, yams in Africa, and rice in China. Human population will now begin to grow with the domestication of animals and the development of agriculture.
3,500
Wheel invented in Mesopotamia
3,100 BCE
Egypt unified. First written language soon developed by Sumerians of Southern Mesopotamia (Bronze Age to 1,000 BCE; bronze made of 90% copper and 10% tin; we know of large tin mining from Afghanistan by looking at ice core samples and measuring the levels of pollution found from the production of bronze.)
2,500
Cities are developed in India, and China, in addition to Mesopotamia and Northeastern Africa; with sedentary civilization comes hierarchy and class division. The Egyptian physician Imhotep describes 200 diseases.
2,000 BCE
Judaism begins with Abraham
1754
Hammurabi’s Code
1478
Hatshepsut comes to throne
1352
Akhenaton comes to throne following Amenhotep III; introduction by Akhenaton of a monotheism focused on the sun
1,250-1,200 BCE
Exodus under Ramses II and Olmec civilization begins; 1177 collapse of multiple civilizations in eastern Mediterranean, including Minoans, Mycenaeans (drought theorized by looking at pollen levels in dug out mud of dried up lagoon), Hittites. Egypt survives. ‘Collapse’ and transformation (including trading networks between Aegeans’ silver, Egyptian and Nubian gold, Hittites and Assyrians, and Afghan tin trade) largely due to climate change, the culmination of three hundred years of drought and widespread famine; with rise of Phoenicians in aftermath, being among the most successful in adapting to new conditions.
509 BCE
Roman Republic
500
Hippocrates, physician
c. 483 BCE
Buddha, Siddhartha Gautama, passes away
425 BCE
Herodotus
411 BCE
Thucydides
327 BCE
Alexander, tutored by Aristotle, reaches India
300 BCE
Euclid writes Elements, a systematic compilation of geometry, number theory, and mathematical logic
240 BCE
Eratosthenes, based at the great library and research center of Alexandria, calculates circumference of Earth (engineer Archimedes and his screw, heliocentric theorist Aristarchus of Samos, mathematician who developed geometry Euclid, are contemporaries). The Musaeum (‘the instituons of the muses,’ since it was dedicated to the muses, the nine goddesses who inspire literature, science, and the arts—the source of knowledge embodies in these—including Clio, the muse of history, daughter of Zeus).
232 BCE
Ashoka Maurya, spreads Buddhism
221 BCE
Qin Dynasty
196 BCE
Rosetta (town of Rashid) made by Ptolemaic ruler, discovered in 1799.
27 BCE
Roman empire and development of first concrete, pozzolana
4 BCE
Birth of عيسى (ʿĪsā)/Jesus
60
Boudica, queen of the Iceni people of Eastern England rebels against Romans
130
Galen, physician works with Gladiators and then the Roman emperor
312
Emperor Constantine converts to Christianity
415
Hypatia, who, teaches astronomy, philosophy, physics, and mathematics, is killed at the direction of the Bishop of Alexandria, Cyril, who is later made a saint.
476
Fall of western Roman Empire
622
Hejira. Year one of Muslim calendar
711
Islam reaches Iberia and India; Chinese invent gunpowder
800
Charlemagne coronation as Holy Roman Emperor and unites much of Europe
850 d.
Al-Khwarizmi introduces Indo-Arabic numerals into Muslim world
869
Zanj Rebellion centering in Basra, southern Iraq
1010
Ibn Sina (Avicenna) Persian physician writes The Book of Healing and The Canon of Medicine
1040 d.
Arab scientist Ibn al-Haythan considered to be one of the first to postulate on the nature of light and optics leading to the concept of the telescope, as well as one of the first researchers to use the scientific method.
1198 d.
Ibn Rushd (Averroes) provides summaries and commentaries on Aristotle and Plato’s Republic
1202
Fibonacci completes Liber abacci, transferring knowledge of Hindu-Arabic numerals and computation via North Africa to Europe, revealing faster and easier use over Roman numerals for finance (Fibonacci sequence described as early as 6th century by Indian mathematicians.)
1315
Birth of Hafiz, Persian poet born in Shriaz
1324
Ibn Battuta begins journey and Mansa Musa of Mali empire will set off on Hajj the next year
1406 d.
Ibn Khaldun historian who wrote the Muqaddimah
1444
First African captives taken to Portugal
1450
Johannesburg Gutenberg moveable type printing press
1453
Fall of Constantinople
1489
Leonardo da Vinci dissects corpses
1492
Columbian Exchange
1517
Martin Luther and Protestant Reformation
1519
Cortez begins conquest of South America
1543
Polish astronomer Copernicus’ heliocentric theory; Girolamo Fracastoro germ theory published three years later.
1526
Mughal Empire
1568
Native Americans push out Spaniards at Joara (Xuala)
1600
Giordano Bruno championed a much more expansive understanding of the Earth’s place in the universe, with the Sun being just one star among all the others, and is burned at stake; Malik Ambar in power
1610
Galileo telescopic observations
1619
Jamestown, VA, 20 Africans; Francis Bacon publishes Novum Organum Scientiarum (‘new instrument of science’) a year later, challenging Aristotle’s methodology of coming to a scientific ‘truth’ by way of argument (using his logical rules), arguing instead that ‘truth’ required evidence from systematic observation. The title of the book was a reference to Aristotle’s Organon, his treatise on logic and syllogism. Lays the groundwork for the ‘scientific method,’ consisting in systematic observation, measurement, experiment, and the formulation, testing, and modification of hypotheses—a proposed explanation for a phenomenon—that can be tested, but provisionally accepted (different from a scientific theory, which is an explanation that can be repeatedly tested … yet accuracy is different from precision).
1628
William Harvey explains the function of heart to circulate blood; Robert Boyle, a founder of modern chemistry, performs controlled experiments and publishes, having devised the vacuum chamber (air pump) and defining the modern idea of an ‘element.’
1640
racial codification begins in Chesapeake
1665
Robert Hooke sees discovers cell observing a thin slice of cork under a microscope he refined
1674
Antoine Leeuwenhoek develops more powerful microscopy to observe and describe single-celled organisms, which he called “animalcules”; these included bacteria, protists, and blood cells
1676
Nathaniel Bacon’s Rebellion; Antoine van Leeuwenhoek, pioneer in microbiology, observes bacteria in water; and Danish astronomer Ole Rømer measures the speed of light by studying the motion of Jupiter’s moon Io. When Earth was moving away from Jupiter in its orbit, Io appeared to move more slowly across the sky, and when Earth was moving toward Jupiter, Io appeared to move more quickly. Rømer deduced that this variation in Io’s apparent motion was due to the finite speed of light. By comparing observations at different times of the year, he estimated that light had a finite speed and calculated it to be roughly 140,000 miles per second (186,282 miles per second). (Further refined by French physicist Hippolyte Fizeau in 1849, measuring with mirrors.)
1687
Isaac Newton three laws of motion and gravitation in Principia
1688
Glorious Revolution, Germantown, PA, Quaker petition against slavery
1712
Thomas Newcomb builds first practical dream engine
1757
John Campbell invents sextant, enables sailors to measure longitude accurately for the first time
1776
Declaration of Independence
1789
French Revolution
1791
Steamboat invented by John Fitch; Bill of Rights ratified
1796
Dr. Edward Jenner introduces idea of vaccinations (taken from Ottoman Empire, taken from India) with small pox on young English boy.
1803
Louisiana Purchase
1804
Haitian Revolution
1808
British and U.S. end slave trade
1814
George Stephenson builds first practical steam locomotive
1824
Peru gains independence
1831
Michael Faraday discovers electro-magnetic current making electric generators and motors AND Nat Turner revolt, North Carolina law then prohibits teaching enslaved to read or write.
1833
Britain abolishes slavery
1835 – Sol, an enslaved African American (of General Hamilton), known to have assisted in setting up escapes for others with Levi and Vestal Coffin almost twenty years earlier uses the Underground Railroad to gain his own freedom.
1839
Alexandre Edmond Becquerel discovered the photovoltaic effect which explains how electricity can be generated from sunlight.
1846
First successful surgical operation using anesthesia by William T.G. Morton; Nitrous Oxide, Ether, and Chloroform
1848
Seneca Falls Convention
1854
Broad Street cholera outbreak in London to be studied by John Snow, shows a clear understanding of Girolamo Fracastoro’s pioneering work on germ theory from 1546. Snow is challenging the dominant miasma theory of ‘bad air’ first proposed by Galen. Smallpox vaccination in use in Europe, with similar treatments in India dating to 1,000 C.E.
1857
Dred Scott case
1859
Charles Darwin Origin of Species; John Brown raid at Harpers Ferry; Louis Pasteur begins to amass evidence to support Germ Theory of Disease
1865
13th Amendment abolishing slavery in the U.S.
1873
James Maxwell publishes Treatise on Electricity and Magnetism
1876
Alexander Graham Bell patents telephone
1880
Thomas Edison patents incandescent electric lamp
1884
Berlin Conference divides up Africa into European colonies
1896
Plessy v. Ferguson, separate but equal made Constitutional in the U.S.
1903
Marie Curie wins Nobel Prize for work on radio activity; Wright Brothers first engine-powered airplane
1905
Albert Einstein theory of special relativity, which is an explanation of how speed affects mass, time, and space, and includes a way for the speed of light (c) to define the relationship between energy (E) and matter where small amounts of mass (m) can be interchangeable with enormous amounts of energy, as defined by E = mc^2; general relativity in 1916, a theory of gravity, with the basic idea that instead of gravity being an invisible force that attracts objects to one another, gravity is a curving or warping of space–the more massive an object, the more it warps the space around it.
1907
Plastic is invented based on synthetic polymer called Bakelite
1908
Dr. John Leal conceived and implements first disinfectant of a U.S. drinking water supply using chlorine; Henry Ford launches Ford Model T
1917
Russian Revolution
1919
Francis Aston pioneers first mass spectrometer, which is used to discover many isotopes.
1920
19th Amendment women’s suffrage; first radio broadcast in Pittsburgh, PA
1928
Penicillin antibiotic discovered by Alexander Fleming; TV sets put in three homes with programming beginning; invention of coolant chemicals for air conditioning and refrigeration
1929
Stock market crash, Great Depression
1934
Karl Popper’s falsifiability; Lev Vygotsky ‘tools and results’
1945
Atomic bomb and end of WWI
1947
India gains independence AND Carbon-14 dating is invented by University of Chicago chemist. Radioactive carbon-14 (an isotope of carbon) has a half-life of about 5,700 years. In 1947 American chemist Willard Libby figured that plants absorb some of the trace carbon-14 from the atmosphere (some nitrogen turning into carbon-14 when hit with cosmic rays) while they absorbed ordinary carbon in photosynthesis. Once the plant died it couldn’t absorb any more carbon of any kind, and the carbon-14 it contained would decay at its usual rate without being replaced. By finding the concentration of carbon-14 left in the remains of a plant, one could calculate the amount of time since the plant had died. With this technique we could determine the age of plant-based artifacts (wood, parchment, textiles) up to 45,000 years old. This has allowed estimates of the age prehistoric dwellings, and ancient documents and clothes, among other things. Also in 1946 a Welsh chemist John Beynon constructed the first mass spectrometer designed to study organic compounds unrelated to petroleum; there was also the invention of the transistor, allowing electronic equipment smaller, leading to computer revolution. So, in this year we’ve got India’s independence, discovery of carbon-14 dating, mass spectrometer to study organic compounds, and the transistor!
1953
Structure of DNA is discovered based on data of Rosalind Franklin
1954
Jean Piaget theory of development AND Algerian war of independence begins AND Brown v. Board of Education
1955
Jonas Salk develops first polio vaccine
1957
Sputnik launched by Soviet Union; NASA formed within a year
1959
Invention of the silicon chip; Abu arrives to U.S. to study engineering at the Georgia Institute of Technology
1960
Woolworth sit-in and 16 African nations gain independence
1962
Thomas Kuhn’s Structure of Scientific Revolutions
1965
Voting Rights Act AND Birth Control pill made legal for married couples
1971
U.S. Voting age lowered from 21 to 18, 26th Amendment
1979
Iranian Revolution
1983
Discovery of HIV virus that causes AIDS
1988
Dr. Lenora Fulani gets on ballot in all fifty states running for U.S. President; the first woman and African American to do so
1989
Fall of Berlin Wall; World Wide Web invented by Tim Berners-Lee
1991
Collapse of the Soviet Union
2003
Complete sequencing of human genome
2008
Barack Obama elected U.S. President; Samina born
2011
Arab Spring
2016
Three nanotechnologists win Nobel Prize in chemistry for building miniature machines out of molecules
2020
COVID-19; Black Lives Matter uprisings
2022
 Fort San Juan, the earliest European settlement in the interior of what is now the U.S. was built in the town of Joara/Xuala (the Berry archeological site) near Morganton in western North Carolina. African-descended Iberians and Africans may have been part of the expedition (no archival records state this but can be inferred from the initial expedition and expeditions of their kind), suggesting early contact and an African Diasporic presence in the Carolinas prior to the seventeenth century.
Fort San Juan, the earliest European settlement in the interior of what is now the U.S. was built in the town of Joara/Xuala (the Berry archeological site) near Morganton in western North Carolina. African-descended Iberians and Africans may have been part of the expedition (no archival records state this but can be inferred from the initial expedition and expeditions of their kind), suggesting early contact and an African Diasporic presence in the Carolinas prior to the seventeenth century.